Extinct Baru crocodile species named years after Alcoota fossil bed discovery
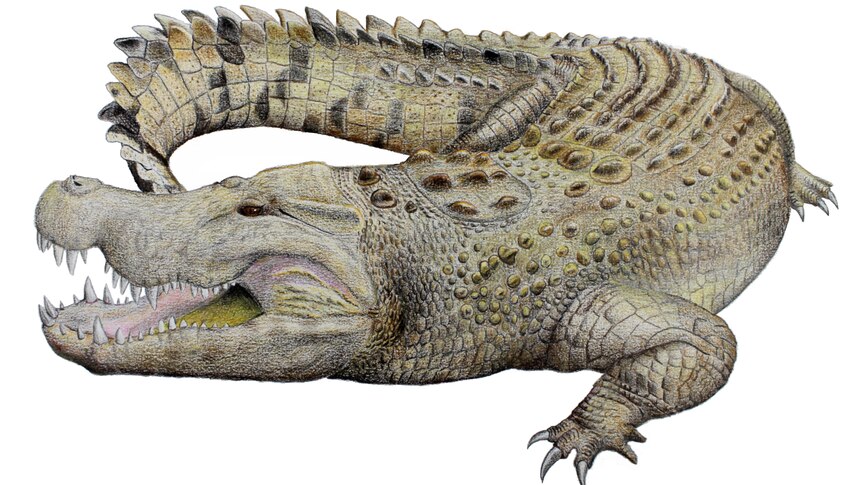
A species of prehistoric crocodile that once roamed the now arid landscape of central Australia has been named.
An article on a “new species of cleaver-headed crocodile” was published today in the online journal Papers in Paleontology.
Lead author and senior curator of earth sciences at the Museum and Art Gallery of the Northern Territory, Adam Yates, named the crocodile Baru iylwenpeny.
Dr Yates said the species name was taken from the Anmetyerre language, meaning excellent and skilled hunter.
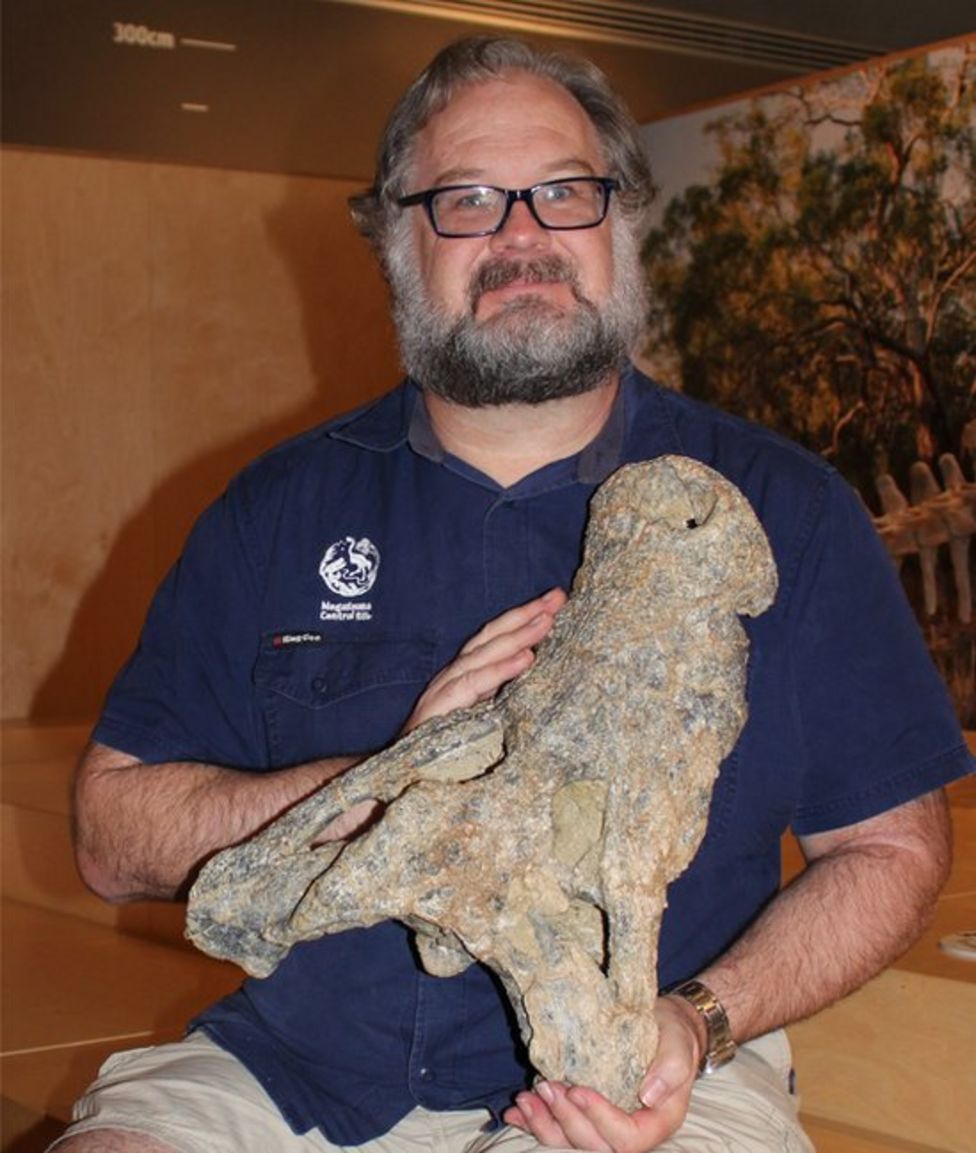

The animal’s skull or holotype was found in 2009.
Dr Yates said it was the most complete skull of a Baru crocodile that had been found.
He said it was also the largest and most dangerous predator scientists had found at the Alcoota fossil bed, about 200 kilometres north-east of Alice Springs.
“We’re very confident that the site dates to an epoch known as the late Miocene,” Dr Yates said.
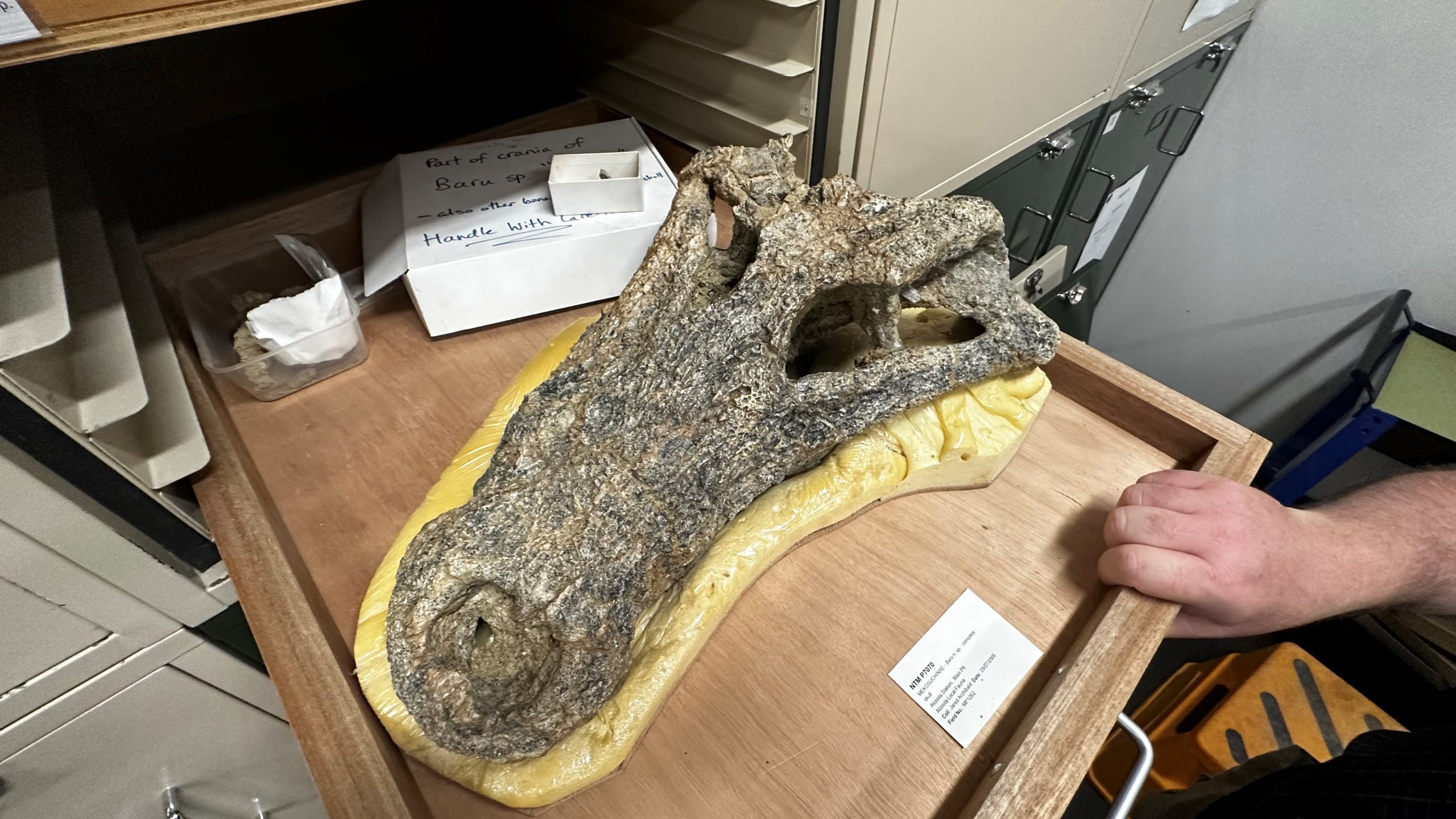

The species was named after the skull was discovered.(ABC Alice Springs: Emma Haskin)
He said the era spanned from about 12 million years ago to five and a half million years ago.
“We think it falls pretty much in the middle of that range at about eight million,” he said.
Dr Yates said the species of Baru was the youngest they had found.
“Baru is actually a relatively common genus, or at least it was in Australia,” he said.
“We find our oldest Baru species also here in the Northern Territory, in rocks that are about 25 million years old.”

Anatomically different
Baru iylwenpeny has anatomical differences from other ancient Baru species.
Dr Yates said the differences gave the creature strength to prey on other megafauna such as the giant flightless bird Dromornis stirtini, which also roamed the same location during the same time.
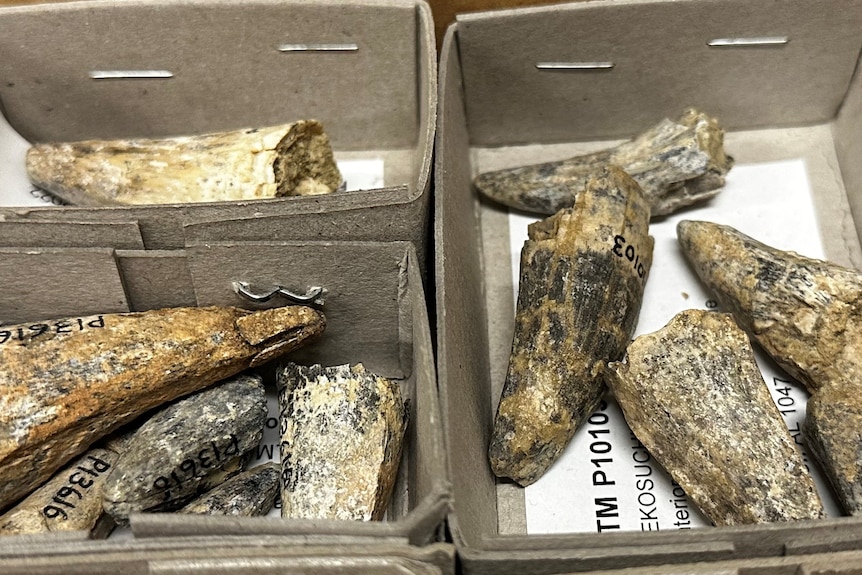

Teeth of the Baru iylwenpeny were found at the Alcoota fossil bed.(ABC Alice Springs: Emma Haskin)
“The main difference between the Alcoota Baru and the other older Barus is that it has bigger back teeth,” Dr Yates said.
He said the newly named species also had a wider snout meaning there was more space at the front of the skull allowing for an extra tooth.
“All of these adaptations are pretty much giving it a bigger, stronger bite,” he said.
Dr Yates said the predator would have preyed on most megafauna.
“It would’ve eaten whatever it wanted,” he said.

‘Just disappears’
Dr Yates said Baru iylwempeny was significant because it was the last of the genus Baru across Australia and therefore not ancestral to modern-day crocodiles which had the genus classification of Crocodylus.
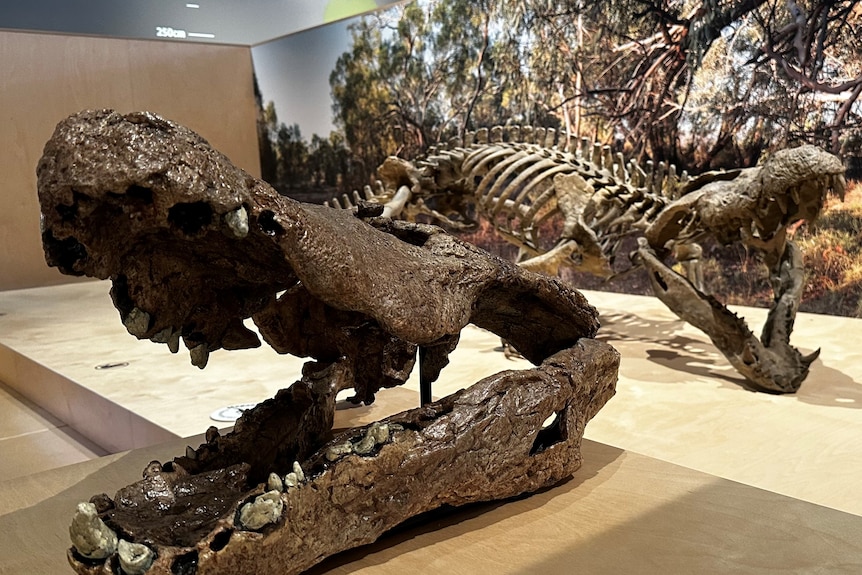

Replicas of Baru iylwenpeny were made by using photogrammetry.(ABC Alice Springs: Emma Haskin)
“It just disappears, but we do continue to get crocodiles,” Dr Yates said.
“So it’s not like the fossil record cuts out.
“The fossil record continues and crocodiles continue but Baru was gone.”
Dr Yates said environmental factors may have played a role in a number of crocodile extinctions across the world at the end of the Miocene epoch.
YouTube Dr Yates studies fossils unearthed in Australia.
He said there was a pulse of rather severe, drying out which may have been somewhat temporary but enough to knock out the inland rivers.
Those climatic changes may have been long enough to cause the extinction of Baru.
“Then conditions returned somewhat, so things got wetter again, the inland rivers flow started to flow again and a cast of new crocodiles moved in to take the place of where Baru once used to swim,” Dr Yates said.





